重构:重组现有代码实体,改变其内部结构而不改变其外部行为的规范式技术。
1. 基于语法的覆盖准则
很多软件构件都使用特定的语法进行描述,例如:
- 程序
- 设计文档
- 有特定格式的输入
一般而言,基于语法的测试有下面两种:
- 有效的:主要覆盖语法的一部分进行测试
- 无效的:使用违反语法的输入进行测试
1.1. 基于文法的覆盖准则
文法通常使用BNF描述,其中包括了下面一些概念
- start symbol
- production
- nonterminal
- terminal
- derivation
基于BNF规则
- Terminal Symbol Coverage (TSC): 测试需求包括文法G中每一个终结符t。
- Production Coverage (PDC): 测试需求包括文法G中每一个产生式p。
- 产生式覆盖能够包含终结符覆盖
- Derivation Coverage (DC): 测试需求包括了每一个从文法G可能推导出来的字符串
2. 变异测试 (Mutation Testing)
- 观点
- 无效的输入应当作为测试用例用于测试。
- 改变产生式并进而生成的有效输入,也值得测试。
- 变异可能使用有效输入也可能使用无效输入。
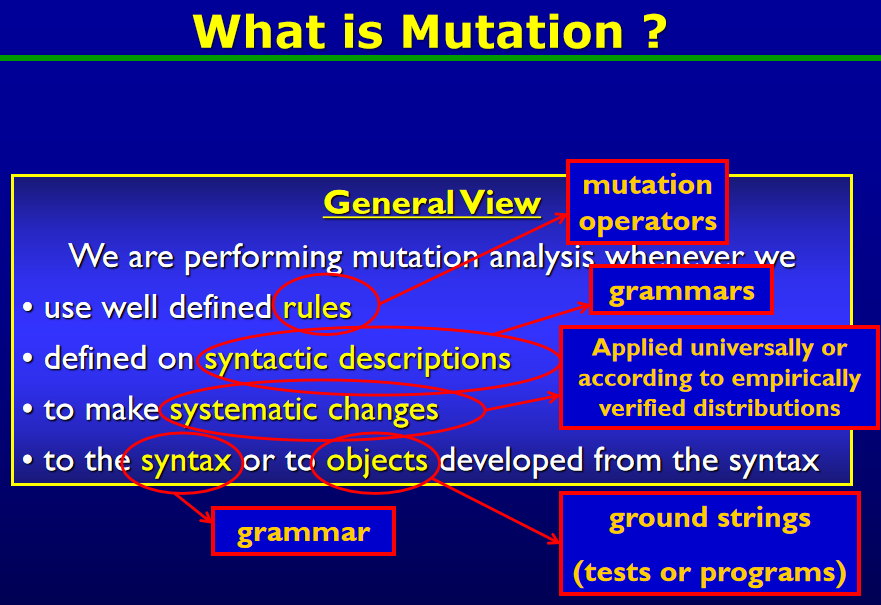
2.1. 术语
- Ground String: 一个符合文法的字符串(derivation得到的结果)
- 程序本身
- 测试输入
- Mutation Operator: 变异运算符,指明语法变异的规则
- 通常用于ground string,但也可以用于:
- grammar
- 动态derivation的过程中
- 通常用于ground string,但也可以用于:
- Mutant: 单次应用变异运算符的结果。
- 变体可能有效也可能无效
2.2. 覆盖准则
A. 若变体有效,则测试目标:杀死变体
Killing Mutants: When a derivation is mutated to produce valid strings, the testing goal is to “kill” the mutants by causing the mutant to produce different output. More formally, given a mutant m ∈ M for a derivation D and a test t, t is said to kill m if and only if the output of t on D is different from the output of t on m.
杀死变体:变体输出和原程序输出不同。
杀死变体通常发生在
- grammar 是编程语言
- strings 是程序
- ground-strings 是原始程序
- Mutation Coverage (MC): 对每一个变体m $\in$ M,测试需求要求kill m。
- 对变体的覆盖等于被杀死变体的数量
- 变体被杀死的数量和总变体数量之比被称为mutation score
杀死变体的test case和检测出fault的test case有一定的关联性。
B. 当变体无效,则测试目标:运行变体以验证行为是否正确,
此时更为简单,因为变异运算符是测试需求。
- Mutation Operator Coverage (MOC): 对于每一个变异运算符,测试需求要求创建一个变异字符串m。
- 每个变异运算符1次
- Mutation Production Coverage (MPC): 对于每一个变异运算符,以及每一个能够应用该运算符的产生式,测试需求要求创建一个变异字符串。
- 每个产生式1次
3. 基于程序的文法 (Program-Based Grammars)
- ground string: 有效的、被测试的程序/函数/方法
-
mutant: 对ground string应用变异运算符后的结果,必须也是有效的
- dead mutant: a test case has killed it
- stillborn mutant: syntactically illegal
- trivial mutant: almost every test can kill it
- equivalent mutant: no test can kill it (和原程序有相同的行为)
根据RIPR模型,基于程序的变异通过变体揭露软件故障,reachability指的是到达变体,infection指的是变体导致程序状态出错,propagation指的是程序最终的输出不正确。
- Reachability : The test causes the faulty statement to be reached (in mutation – the mutated statement)
- Infection : The test causes the faulty statement to result in an incorrect state
- 转移语句的变体:pc寄存器的值的trace是否和源程序一致,即执行路径是否一致
- 赋值语句的变体:赋值什么时候有区别
- Propagation : The incorrect state propagates to incorrect output
- Revealability : The tester must observe part of the incorrect output
弱变异放松了“杀死”的要求,只需要包括reachability和infection,不需要propagation。相应的原本的要求propagation的定义被修改为强杀死变体:
- weakly killing mutants: Given a mutant m ∈ M that modifies a location l in a program P, and a test t, t is said to weakly kill m if and only if the state of the execution of P on t is different from the state of the execution of m on t immediately after l.
- strongly killing mutants: Given a mutant m ∈ M for a program P and a test t, t is said to strongly kill m if and only if the output of t on P is different from the output of t on m
下面给出覆盖准则
- Strong Mutation Coverage (SMC): 对每一个变体m ∈ M,测试需求要求强杀死m。
- Weak Mutation Coverage (WMC): 对每一个变体m ∈ M,测试需求要求弱杀死m。
3.1. 示例
1 | |
1 | |
- 可达性:x < 0
- 感染: x < 0 且 x != 0
- x = -6即可弱杀死
- 传播性
- x非偶数
- x = -1强杀死
3.2. 本质
如果软件包含一个故障,则应当有一些变体仅能被一个能测试出该故障的测试杀死。