Scale-out Parallelism, Elasticity, and Caching.
- focus
- parallelism
- locality
- metric
- throughput
- latency
1. setting worker number for web server
- Parallelism: use all the server’s cores
- Latency hiding: hide long-latency disk read operations
- Concurrency:
- many outstanding requests;
- service quick requests
- Footprint: don’t want too many threads so that aggregate working set of all threads causes thrashing
2. dynamic content
dynamic content: response is not static page but the result of application logic running in response to a request.
2.1. scale for higher throughput
scripting language performance is terrible, therefore we can try scale the web servers for higher throughput
requests -> load balancer -> multiple web server <-> database
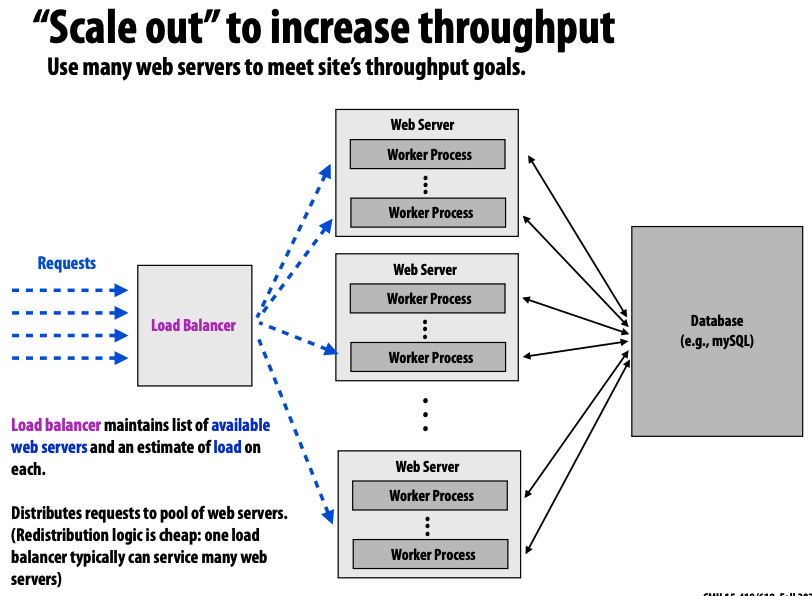
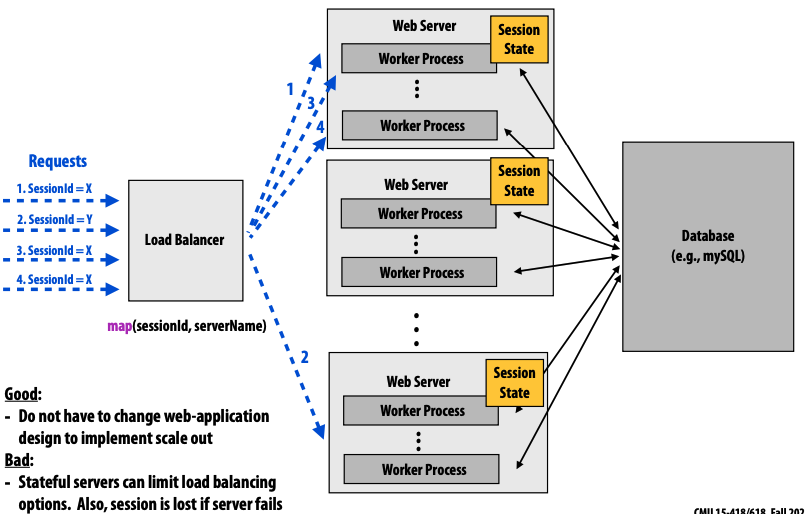
- prob: how to deal with consistency state of sessions
- approach 1: session affinity
- all requests associated with a session are directed to the same server
- load balancing is poor
- do not have to change web-application design to implement scale out
- approach 2: persist session state into database, namely stateless servers
- load balancing is not a problem
- web server is easy to scale
- db becomes the bottleneck
- approach 1: session affinity
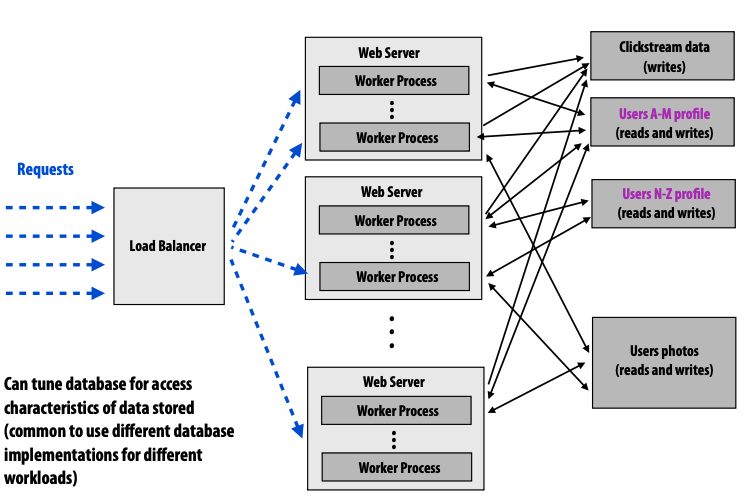
- prob: scaling out a databse
- replicate: read-only replicate data and parallelize reads
- write is still a problem
- consistency issue
- partition
- replicate: read-only replicate data and parallelize reads
2.2. how many web servers do we need
- observ: site load is bursty
- provisioning site for the average case load -> poor quality of service during peak usage
- provisioning site for the peak case load -> many idle servers most of the time
- solution: elasticity
- foundation: server is stateless
- sites automatically adds or removes web from/to worker pool based on measured load
- source of servers available on-demand: aws, Azure, etc
2.3. reuse and locality
- cache: cache commonly accessed objects
- between web server and database
- cache consistency problem
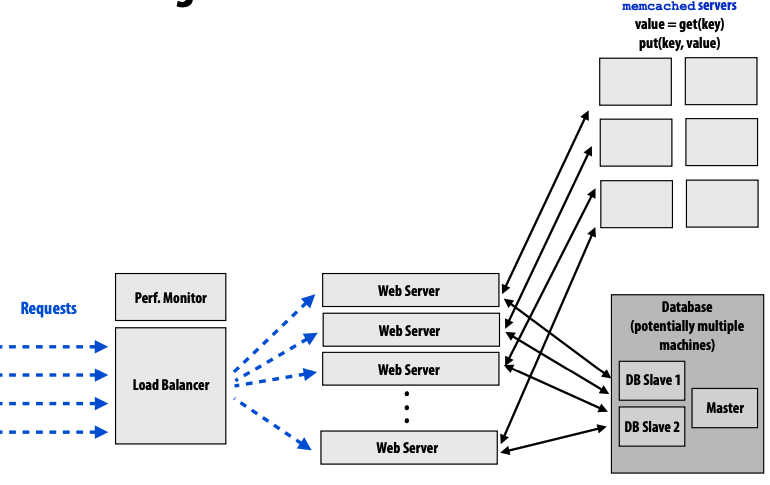
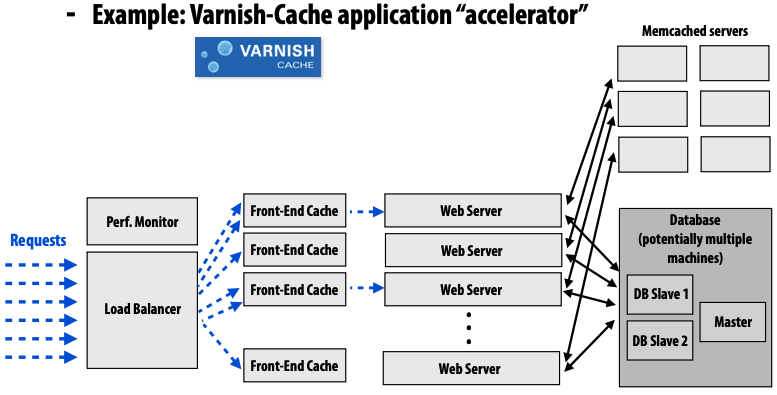
- front-end cache: cache web server responses
- reduce load on web servers
- between load balancer and web server
- content distribution networks(CDN): images and videos
- redirect request url to CDN servers based on locality information
- higher bandwidth
- lower latency
- redirect request url to CDN servers based on locality information