内存一致性: 当多核系统存在数据竞争(对同一个内存地址的两次访问至少有一次是写操作)时,整个系统会表现出怎样的行为。内存一致性模型实际上定义了某种具体架构下内存系统的可见行为集合。
What is the correct behavior for a parallel memory hierarchy?
- reading a location should return the latest value written
- within a thread: defined by program order
- across threads: defined by a valid interleaving of threads
1. memory correctness
- part 1: cache coherence
- ensure the correctness ordering of a given cache block
- part 2: memory consistency model
- ensure the correctness ordering of separate cache blocks
2. why is this so complicated?
- fundamental issue: performance
- the processor aggressively reorders instructions to hide memory latency
- write buffer
- invalidation queue
- 线程内部同一个内存地址的访问的顺序性被保留,但是不同内存地址的访问可能被重排
3. sequential consistency
1 | |
SC: (0, 0), (0, 1), (1, 1)
1 | |
SC: (0, 1), (1, 0), (1, 1)
TSO: (0, 0)
- a approach to implement SC
- first, implement cache coherence
- second, for each processor, delay start of memory access until previous one completes
4. operation complete
- memory read: a read completes when its return value is bound
- write complete: a write completes when the new value is “visible” to other processors
- a.k.a commit to memory order
5. memory consistency
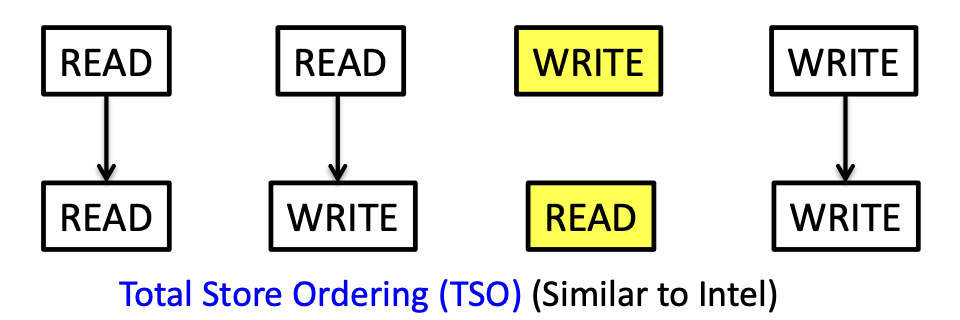
- TSO: allows store buffering, may delay the propagation of write operations to other cores
5.1. identifying data races and synchronization
- conflict accesses
- access same location
- at least one is a write
- order accesses
- program order (po)
- dependence order (do): op1 -> op2 if op2 reads op1
1 | |
- data race
- two conflicting accesses on different processors
- not ordered by intervening accesses
- properly synchronized programs
- all synchronizations are explicitly identified
- all data accesses are ordered through synchronization
5.2. MFENCE
- does not begin until all prior reads and writes from that thread have competed
- no subsequent read or write from that thread can start until after it finishes

MFENCE operations do not push values out to other threads, they simply stall the thread that performs the MFENCE
- LFENCE: serializes only with respect to load operations
- SFENCE: serializes only with respect to store operations
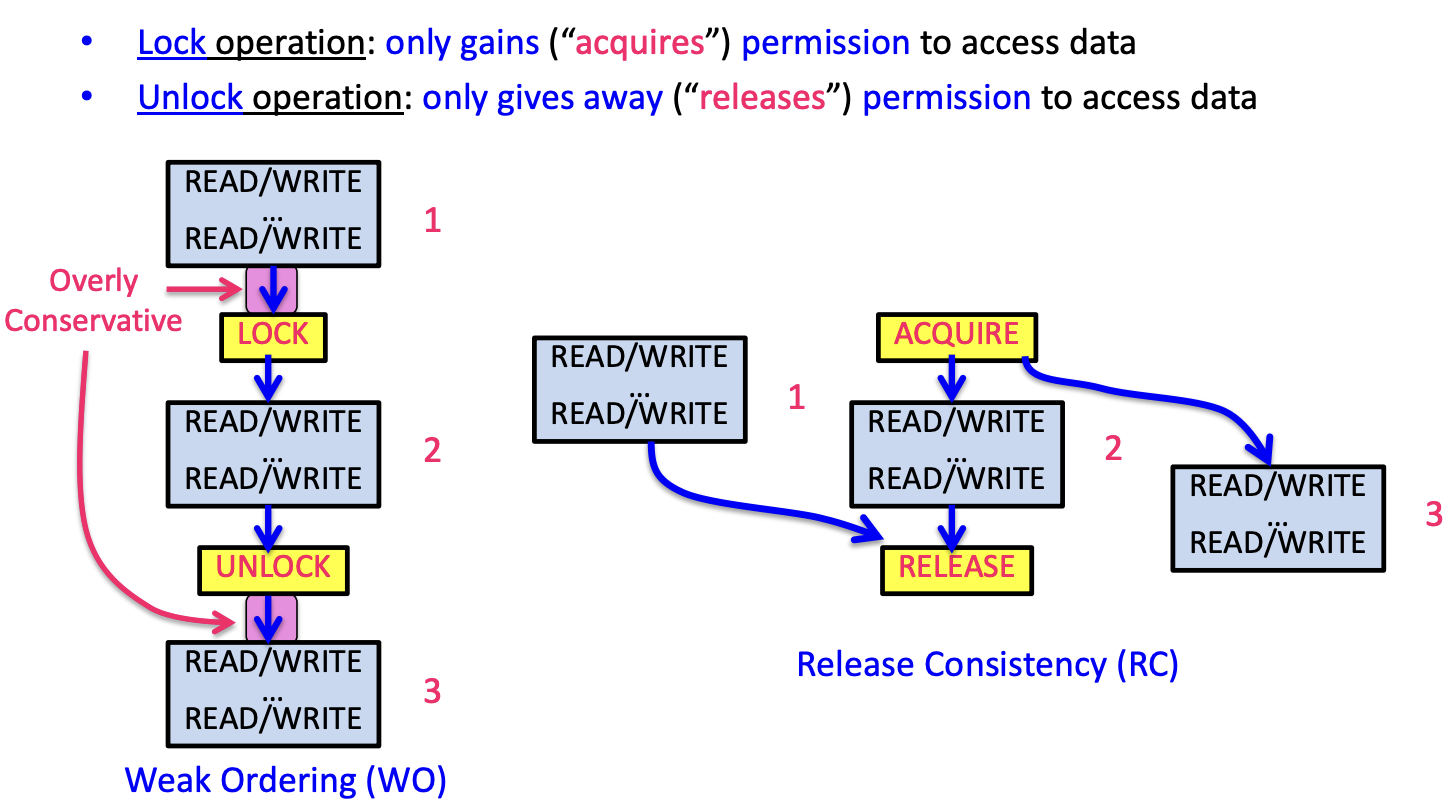
5.3. other kinds of consistency
- weak ordering (WO)
- release consistency (RC)